Soft Tissue Grafting
Understanding Soft Tissue Grafting
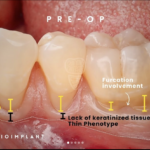
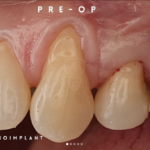
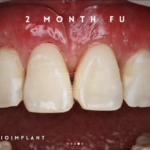
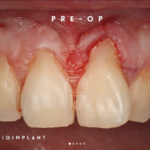
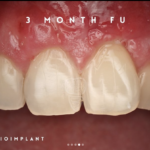
Soft tissue grafting is a common and effective procedure to address gum recession, which can occur due to periodontal disease, trauma, aging, over brushing, and poor tooth positioning. Gum recession can lead to tooth-root exposure, making eating hot and cold foods uncomfortable, increasing decay risk, and altering the aesthetic appearance of your smile. The primary goal of soft tissue grafting is to either cover exposed roots or thicken existing gum tissue to prevent further tissue loss.
Types of Soft Tissue Grafts
There are three common types of soft tissue grafts:
- Free Gingival Graft:
- A strip of tissue is removed from the roof of the mouth and stitched to the grafting site to promote natural growth.
- Commonly used for thickening existing tissue.
- Connective Tissue Graft:
- For larger areas or root exposure, subepithelial tissue is used.
- This tissue is removed from a small flap in the mouth and sutured to the grafting site.
- Most common treatment for root exposure.
- Pedicle Graft:
- Involves “sharing” soft tissue between the affected site and adjacent gum.
- A flap of tissue is partially cut away and moved sideways to cover the root.
- Excellent results due to the tissue’s blood vessels remaining in place.
Reasons for Soft Tissue Grafting
Soft tissue grafting is a versatile procedure with numerous benefits:
- Increased Comfort: Covers exposed roots, reducing sensitivity and discomfort from hot, cold, or warm foods.
- Improved Aesthetics: Re-augments gums to create a more symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing smile.
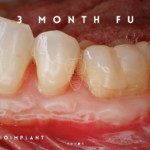
- Enhanced Gum Health: When combined with deep cleaning procedures, it halts tissue and bone loss, protecting exposed roots from further complications.
The Soft Tissue Grafting Treatment Process
- Initial Cleaning:
- Deep cleaning above and below the gum line to remove calculus (tartar).
- Grafting Procedure:
- Typically performed under local anesthetic, depending on the size of the grafting area.
- A small incision is made at the recipient site to create a pocket.
- A split thickness incision is made, and donor tissue is placed between the two sections.
- The donor tissue strip is generally larger than the incision, leaving some excess.
- Application of Growth Factors:
- Platelet-rich growth factors and tissue-stimulating proteins may be applied to stimulate natural tissue growth and promote healing.
- Suturing and Protection:
- The wound site is sutured to prevent shifting, and surgical material is placed to protect the sensitive area.
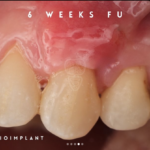
- Gum uniformity and substantial healing occur over the first six weeks post-procedure.
Schedule Your Soft Tissue Grafting Consultation
If you’re experiencing gum recession or discomfort due to exposed roots, soft tissue grafting may be the solution you’ve been searching for. Our specialized periodontist, Dr. Choi, provides personalized treatment plans tailored to restore healthy gums, ensuring patient comfort and optimal results.
Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards better gum health and a more confident smile.